When we see a beautifully painted car gleaming in the sunlight, we often overlook the intricate processes and technologies behind that flawless finish. Automotive painting is one of the most critical stages in car manufacturing, balancing aesthetics, functionality, and durability. In this blog, we’ll dive into the step-by-step journey of painting a vehicle in an automotive factory, the importance of inspections, and the role of automation in ensuring perfection.
In what phases does the Automotive Painting Process consist of?
The painting process in modern automotive factories is highly sophisticated and automated. Although specific steps may vary between manufacturers, the general workflow follows a structured sequence:
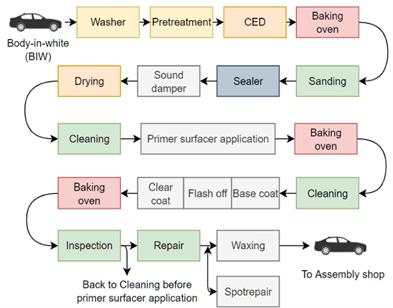
Body-in-White (BIW) Preparation: The car body undergoes rigorous preparation before painting. This includes washing and degreasing to remove dirt, oil, and contaminants. Even the smallest particles can compromise the paint’s adhesion and quality.
Pre-treatment and Electrodeposition Coating (CED): In an electrodeposition process, the car body is submerged in a bath containing rust-resistant paint. Positively charged paint particles adhere uniformly to the negatively charged metal, providing a corrosion-resistant primer coat.
Baking and Sanding: After CED, the body is baked in an oven to harden the primer. Sanding smoothens the surface, ensuring a flawless foundation for subsequent coats.
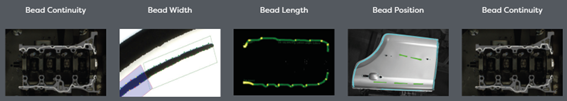
Sealing and Sound Dampening: A Sealer is applied to steel joints to waterproof and soundproof the vehicle. This step also improves the aesthetics of areas like wheel wells. Eines Sealer Check can inspect the sealer’s coverage and continuity, ensuring no gaps or inconsistencies.
Middle Coating: A middle coat—typically in shades of white, gray, or dark gray—acts as a foundation for the topcoat, enhancing the final color’s vibrancy. Its hue is chosen based on the desired exterior color.
Basecoat and Clearcoat Application: The basecoat provides the car’s primary color, while the clearcoat adds gloss and protects against UV radiation, scratches, and environmental elements. Cutting-edge airless coating techniques improve paint adhesion and reduce environmental impact.
Drying and Curing: Each layer is baked at approximately 150°C (300°F) for 20 minutes, ensuring durability and a smooth finish.
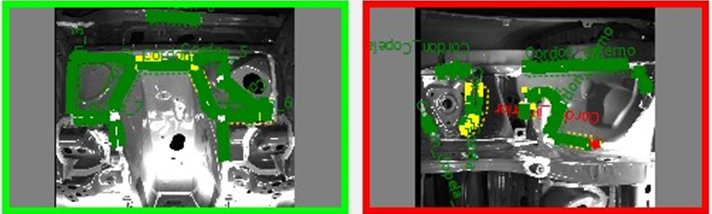
Inspection: Manual inspections, while traditional, are less reliable and efficient. Automated systems like the Eines ESFI Tunnel have revolutionized this step by using deep learning technology to detect paint defects with high precision.
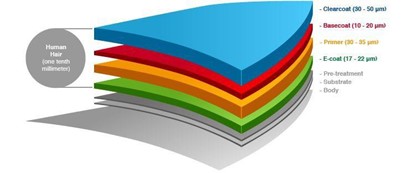
As you may have noticed, there are several bases during the painting process and therefore several layers of product that are applied during the process. The result is carefully arranged layers, all of which together are only slightly thicker than an average human hair.
The Eines ESFI Tunnel be installed at different stages of the painting process, to control the correct application of each layer, and to avoid the build-up of defects.

Repair: Any imperfections identified are repaired using automated repair processes guided by the defect data provided by the tunnel. Eines has collaborations with system integrator experts like ICEMI, and technological partners for consumables like 3M, with the 3M Finesse-it
Why Inspections and Repairs Are Crucial?
A flawless paint job is essential for both aesthetic appeal and long-term durability. The ESFI Tunnel, for example, inspects the surface by analyzing light reflections to detect even the smallest inconsistencies. This ensures:
- Improved Quality Control: Consistency across vehicles.
- Higher Efficiency: Automation reduces time and human error.
- Sustainability: Minimizes material waste by pinpointing and addressing defects early.
Defect data generated during inspections drives automatic repair systems, enabling factories to replicate the original factory finish in a seamless and efficient manner.
How will be the Paint Shop of the future?
The automotive paint shop is evolving rapidly with advancements in technology and sustainability. Five key pillars define the paint shop of the future:
Efficiency: Fully automated lines with optimized equipment and intelligent software.
Innovation: Incorporating the latest technologies for better outcomes.
Flexibility: Adapting to various vehicle models and production demands.
Sustainability: Eco-friendly products and processes to reduce environmental impact.
Quality and Service: Superior results backed by global support throughout the paint shop’s lifecycle.
Digitalization is integral to these pillars. Advanced software solutions like DXQ systems enable predictive analysis, process optimization, and real-time monitoring.
Conclusion: Knowledge Drives Excellence
Mastering the automotive painting process is essential for achieving exceptional results, whether in a factory setting or a workshop. By understanding each stage—from cleaning and priming to inspection and repair—you can better appreciate the technologies and techniques that create those showroom-worthy finishes. Automated systems like the ESFI Tunnel play a crucial role in ensuring consistency, efficiency, and sustainability.
As the automotive industry moves toward a fully digitalized future, the paint shop will continue to evolve, setting new standards for quality and environmental responsibility. Stay informed, stay innovative, and always strive for perfection in every coat.
Fonts
Streitberger, H.-J.; Dossel, K.-F. Automotive Paints and Coatings; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3527309713.






